10/08/19 Lytic & Lysogenic Cylces Poster
Make a poster showing the lytic and lysogenic cylces of bacteria.
10/10/19 KURU VIDEO below.
Watch the video. Then you can take the quiz over the video.
Epidemics Webquest lhttp://www.biologycorner.com/projects/outbreak/index.html
Review nutrition and the digestive system
• the nutrition terms organic molecule, protein, lipid, simple and complex carbohydrates, starch, calories, fiber, vitamins and minerals, portions, serving size, body mass index, glycemic index, metabolism
• the new federal guidelines for eating healthy in schools
• the role of the digestive system
• problems that may arise from poor nutrition: obesity, high blood
pressure, heart attack, strokes, type 1 and 2 diabetes
• the following organs: mouth, salivary glands, teeth, esophagus,epiglttis, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder,large intestine, colon, anus
digestive terms: mechanical digestion; chemical digestion;
the enzymes amylase pepsin HCL bile insulin
• problems that may arise in the digestive track: appendicitis, choking,consitpation, diarrhea, vomiting ulcers
Tri-Fold Pamphlet or Glog
Title it with animal's name and scientific name.
IUCN Red Listing For Example: Critically Endangered, Endangered, Threatened etc…
Global Population
Why does the animal have its’ current listing? What anthropogenic activities contribute to the decline of this animal’s population? (Are invasive species to blame? Pollution? Habitat Destruction? )
Animals with a limited range or specialized habitat are more vulnerable to habitat and ecosystem disruption. What is this animals range and does it contribute to the decline of the population? What is this animals habitat? Is it highly specialized and does that contribute to population problems?
Include a model to show the flow of energy in your animal's ecosystem. Analyze the model. Which type of animals require a larger range: producers, primary, secondary or tertiary consumers? How does this affect population?
Animals with a highly specialized diet cannot adapt to changes in their environment as readily as those with a varied diet. Does this animals’ diet contribute to the population decline?
What is the captive population of your species?
What adverse affects or challenges face your species captive population?
Part II to be completed during and after our trip to TWP.
During the trip to TWP take a picture of your species and a short video. Post it to your glog.
Take special note of the habitat provided by TWP. How is it like the wild habitat? How does it differ?
What types of interactions with other animals of the same species are provided compared to what the animal might experience in the wild?
Also note the diet of the captive animal as compared to what it's wild counterparts would consume. What are the differences?
What are the pros and cons of breeding captive populations?
Rat Dissection Virtual http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/rat_dissection02.html#.U0LTaahdWSo
The Role of Reproduction
• the following male sex cell and organs: sperm, testes, scrotum, vas
deferens, prostate, urethra, penis
• the following female sex cell and organs: egg, ovaries, fallopian
tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina
• problems that may arise in the reproductive track: ovarian cysts,
cervical cancer, testicular cancer, prostate cancer
• changes that occur in mother and child during first, second, and
third trimesters
• the medical terms: pregnancy, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy,
preeclampsia
• various forms of birth control
Review the Endocrine System
• the role of the endocrine system and hormones
• the following glands: pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenal,
testes, ovaries, pancreas, liver
• the following hormones: testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, human
chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), insulin, glycogen
• the glycemic index (again)
• problems that may arise: type 1 and 2 diabetes
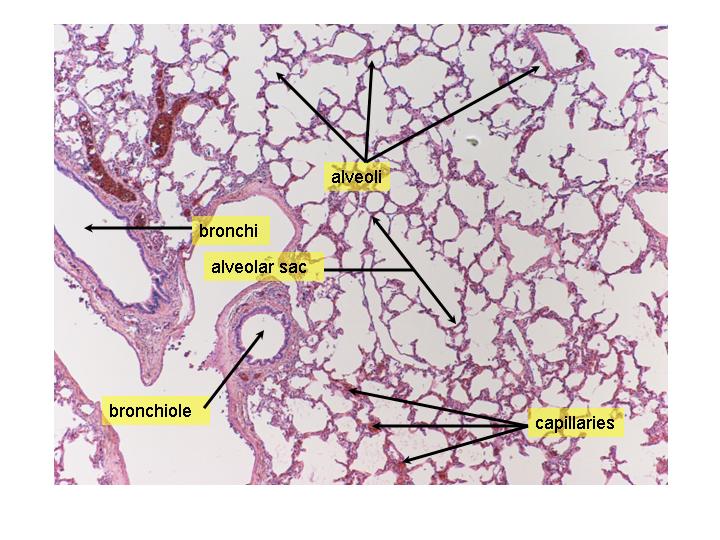
REVIEW THE ROLE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
• the role of the respiratory system
• the following organs: nasal cavity, trachea, epiglottis, bronchi tubes,
lungs, alveoli, and diaphragm
• problems that can arise in the respiratory system: pneumonia,
bronchitis, asthma, hiccups
• the term lung capacity
Review the circulatory system:
• the role of the circulatory system
• the following blood vessels: veins, arteries, and capillaries
• the following parts of the heart: superior and inferior vena cava,
right atria, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, left atria,
left ventricle, and aorta
• the following parts of blood: red blood cells, white blood cells,
plasma, and platelets.
• problems that may arise from poor nutrition or genetics: high
blood pressure, heart attack, strokes, hemophilia, and sickle cell anemia.
Review the immune system.
• the role of the immune system
• the following organs: spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and lymph nodes
• the following white blood cells and their functions: T-cells and
B-cells
• the difference between viral infections and bacterial infections
• the terms: vaccines, antibodies, and antigens
• problems that may arise in the immune system:
• viral sexually transmitted infections: HIV, HPV, herpes simplex I
and II, hepatitis C;
• bacterial sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, gonorrhea,
syphilis
• other infections or health conditions of student interest: chicken
pox, mononucleosis, measles, leukemia, autoimmune disorders
Medical School Follow 6 Medical Students Through a Year of Medical School
Link to Class Wikispace Echinoderm Glogs
Cryafish
http://shapeoflife.org/video/terrestrial-arthropods-conquerors
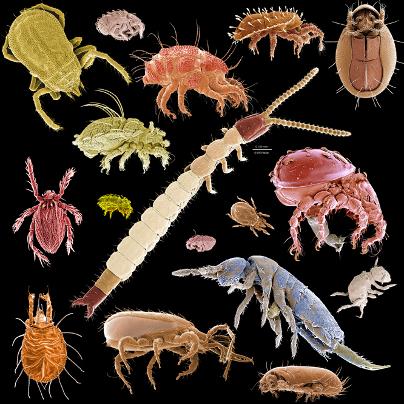
MICROARTHROPODS
Bellwork 11/6 Find a picture of the part or parts assigned to you and write a short description of what it is used for by arthropods. This will help us when using our kwik key.
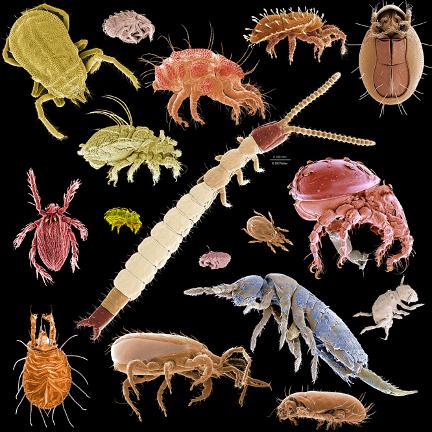

Micro-Arthropod Extraction Lab
Background Microarthropods range from 0.1 to 5 mm in size-barely visible to hman eyes. Dozens of microarthropod species can be unearthed in one shovelful of soil. Discover these hidden animals in this investigation.
1. Build Berlese Filters (Instructions for Berlese Filter)
2. Collect Soil Samples
3. Add Samples to Berlese Filters
4. Wait 24 to 48 hrs for arthropods to migrate away from the light into the ethanol.
During the waiting period we will conduct "mini labs" and work on other adv.bio assignments as time allows.
5. Identify the arthropods using Kwik Key
Soil Collection for Micro-Arthropod Extraction
(1) remove a 25cm x 25cm x 5cm deep (10" x 10" x 2") sample of soil (including any plant litter on surface - plant litter NOT included in the 5cm depth) and gently place in plastic bag.
In order to minimize crushing of soil fauna, extract the soil sample by:
(a) marking out the 25cm x 25cm margins on the soil with the end of a trowel
(b) digging a trench 25cm long by 30cm deep along one edge
(c) cut the 4 edges vertically of the 25 x 25 markings to a 10-15cm depth
(d) insert the trowel horizontally under the 25 x 25 markings at a 5cm depth
(e) lift the sample (usually more-or-less in a single piece) into a ziplock bag